Indoor air pollution causes and effects
Indoor air pollution is a serious problem and affects millions of people around the world. According to new data from the World Health Organisation (WHO), nine out of ten people breathe air with high levels of pollutants. Updated estimates show that seven million people die each year from ambient (outdoor) and domestic air pollution, which means that Indoor Air Quality is crucial to our health and well-being.
If you feel safe at home, let me ask you something…
When was the last time you were tired, disoriented, or uncomfortable by being in a place with intense odors or rare air?
Many factors can contribute to Indoor Air Pollution, including the natural degradation of furniture/electronics, chemicals from cleaning and personal-care products, tobacco, and floor coverings, among other consumer products that emit gas pollutants or particle matter (dust).
These pollutants can cause diverse health problems, including asthma, respiratory disease, heart disease, and cancer.
What pollutes the air in your home?
Did you know that we humans would spend approximately 90% of our lives in indoor spaces? (housing, workplaces, leisure or cultural spaces, schools…) and What about we breathe up to 65% of the outdoor contaminants indoors? Our homes, schools, offices, and other indoor places are 2 to 5 times more polluted than in the streets of our cities!
We all know that tobacco smoke could be the principal air pollutant in the home and that passive smokers are at increased risk of developing respiratory disease and heart disease. Children are particularly vulnerable to tobacco smoke at home, and exposure to it can increase their risk of asthma and pneumonia.
But, What about the other pollution sources?
-
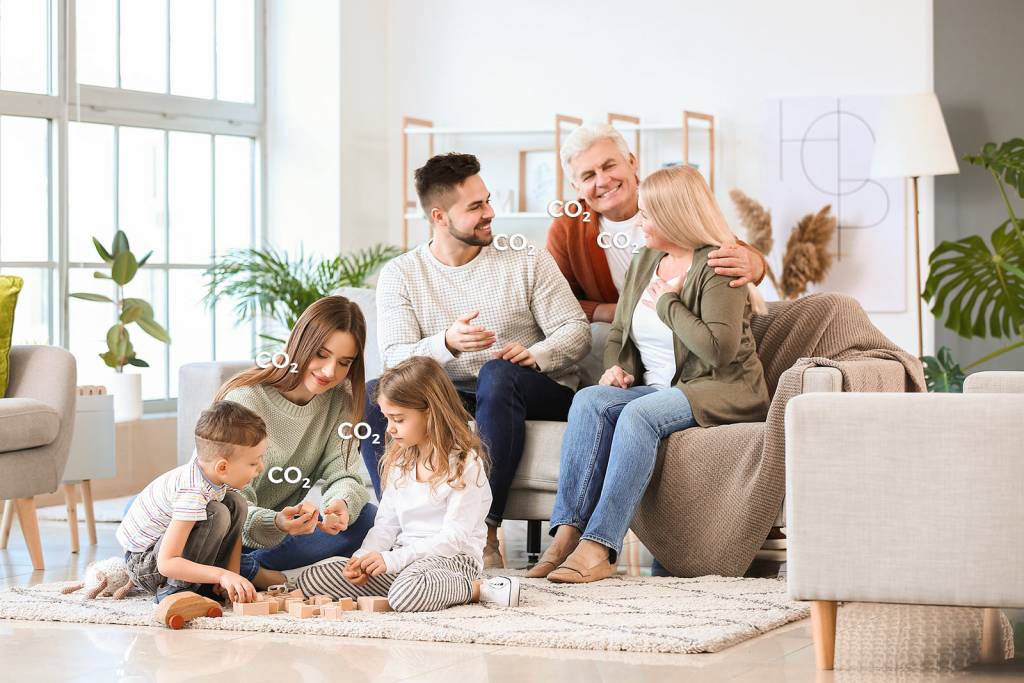
Carbon dioxide
Is a gas that is produced when humans breathe. When the concentration of CO2 in a room is high (e.g., in enclosed spaces full of people), it can cause symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, and decreased concentration. It is, therefore, necessary to ensure adequate ventilation and air supply to dilute the pollutants, and simply opening a window could be enough (if we live in cities with good air quality).

-
The Chemicals
use to clean our homes/offices/schools can also contribute to air pollution, as many of these products contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that include carbon, hydrogen, sulfur, or nitrogen dioxide amid other toxic gas pollutants.
Elevated exposure to these chemicals can cause a wide range of adverse health effects, such as irritation of the eyes, skin, and throat, other than headaches, dizziness, and fatigue.
It is necessary to select household cleaning products carefully and consider safer and more environmentally friendly alternatives, such as natural cleaning products ( such as vinegar and baking soda). It is also essential to always follow proper storage and use instructions to avoid accidents and unnecessary contamination.
-
Dust and mold
build-up in the home can also contribute to air pollution. Dust can contain allergens that can trigger asthma attacks, while mold can release spores that can provoke respiratory health problems in sensitive individuals, such as allergies and asthma.
-
Heating
is one of the most significant sources of urban air pollution as they use fossil fuels, such as gas and oil, to generate heat. The combustion of these fuels produces exhaust gases, such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and fine particulates, which are released into indoor air.
-
Kitchens
are another significant source of household air pollution. A recent study indicates that gas stoves in poor condition can release unburned methane, besides producing other gases such as formaldehyde, carbon monoxide, and nitrous oxides. These gases can trigger asthma, coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
We know how important your health is to you and your family, so we will soon be launching a product that will help you reduce pollution in your home.